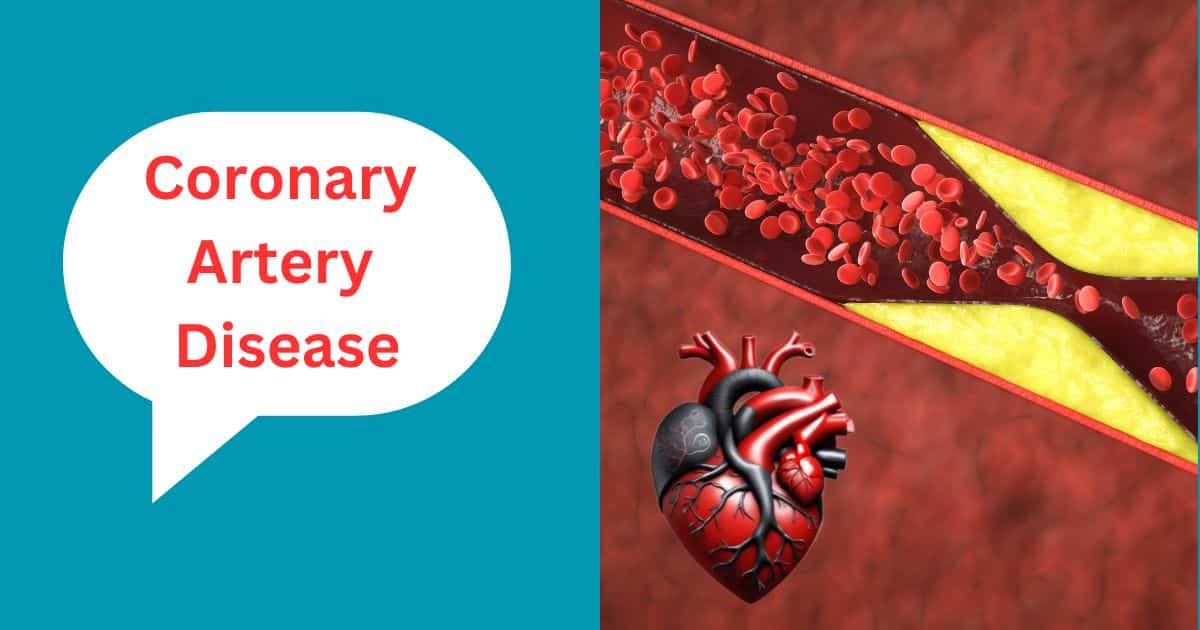
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening cardiovascular condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a type of heart disease that occurs when the blood vessels supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, known as coronary arteries, become narrowed or blocked. This article explores the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies associated with Coronary Artery Disease.
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
The primary cause of Coronary Artery Disease is atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances on the walls of the coronary arteries. This accumulation forms plaques that can narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow to the heart. Over time, these plaques may rupture, leading to the formation of blood clots that can further block the arteries and cause heart attacks.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
When your heart doesn’t get enough arterial blood, it may show many symptoms. The symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease can vary, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms until a heart attack occurs. Common symptoms include:
Chest Pain or Discomfort: Often described as angina, this pain may radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder, or back.
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or emotional stress, may indicate reduced blood flow to the heart.
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired, weak, or lightheaded can be a symptom of reduced blood flow to the heart.
Other Symptoms:
- Heaviness
- Tightness
- Burning
- Squeezing
- Pain in the arms or shoulders
- Sweating
- Dizziness
Women may also experience the above symptoms plus nausea, vomiting, back pain, and jaw pain.
Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease
Several risk factors contribute to the development of Coronary Artery Disease. These include:
Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage blood vessels, accelerating the progression of atherosclerosis.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension increases the workload on the heart and can damage the arteries and promote the development of plaques.
High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, contribute to plaque formation.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing CAD due to elevated blood sugar levels that can damage blood vessels. If you need any diabetes supplements, then GlucoTrust and Glucofort are great options.
Obesity and Inactivity: Being overweight or leading a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of CAD. By the way, if you are looking for a weight-loss supplement, Alpilean is a great choice.
Age and Gender: The risk increases with age, and men are generally more susceptible than women, although women’s risk rises after menopause.
Family History: Individuals with a family history of CAD are at a higher risk, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease
Preventing Coronary Artery Disease involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors. Strategies include:
Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for CAD. Quitting can significantly reduce the risk and improve overall health.
Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure and cholesterol levels are crucial in preventing CAD.
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week.
Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to promote emotional well-being. If you need an online yoga program, Shapeshifter Yoga is a superb yoga program.
Final Thoughts
Coronary Artery Disease is a serious health concern, but adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors can significantly reduce the risk of its development. Regular medical check-ups, early detection, and appropriate interventions are essential for maintaining heart health and preventing complications associated with CAD. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your heart health, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.